I wanted to start a series of how to use AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) to create infrastructure on Amazon. In our first example we will tackle the fundamental of a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). We will be using AWS CDK to create a VPC in C#. You may wonder what about CloudFormation json or yaml files that Amazon allows one to create infrastructure that you maybe very comfortable in doing it, is CDK replacing that?
What about CloudFormation?
AWS CloudFormation enables you to do many things, below are some of the things that the CDK allows us to do. (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/home.html)
- Create and provision AWS infrastructure deployments predictably and repeatedly.
- Leverage AWS products such as Amazon EC2, Amazon Elastic Block Store, Amazon SNS, Elastic Load Balancing, and Auto Scaling.
- Build highly reliable, highly scalable, cost-effective applications in the cloud without worrying about creating and configuring the underlying AWS infrastructure.
- Use a template file to create and delete a collection of resources together as a single unit (a stack).
Rest assure that Cloudformation is here to stay and CDK is not a way to replace it, but think of it in terms of a SDK for you to create infrastructure in the language of your choice.
Ok tell me more about CDK?
The advantage of AWS CDK is that you can define your cloud resources in a familiar programming language. As it stands the AWS CDK supports TypeScript, JavaScript, Python, Java, C#/.Net, and (in developer preview) Go lang. As a developers you can use one of the supported programming languages to define reusable cloud components known as Constructs. You compose these together into Stacks and Apps. The other advantages of the AWS CDK include listed below:
- Use logic (if statements, for-loops, etc) when defining your infrastructure
- Use object-oriented techniques to create a model of your system
- Define high level abstractions, share them, and publish them to your team, company, or community
- Organize your project into logical modules
- Share and reuse your infrastructure as a library
- Testing your infrastructure code using industry-standard protocols
- Use your existing code review workflow
- Code completion within your IDE
What is an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)?
Before we get started I wanted to provide some information on VPC. With Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), you can launch AWS resources in a logically isolated virtual network that you define. You have complete control over your virtual networking environment. This includes selecting your own IP address range, creating subnets, and configuring route tables and network gateways. And the reason to use a VPC is that your applications and database will be accessible over the network, but you may not want them to be accessible to everyone over the internet. Using an Amazon VPC, you can control who accesses which resources over the network.
Show me what we are building
The diagram below shows us the VPC that contains two Availability Zones, and in each one you will see there are 2 subnets a public and a private subnet. The public subnet will allow internet traffic while the private will not.
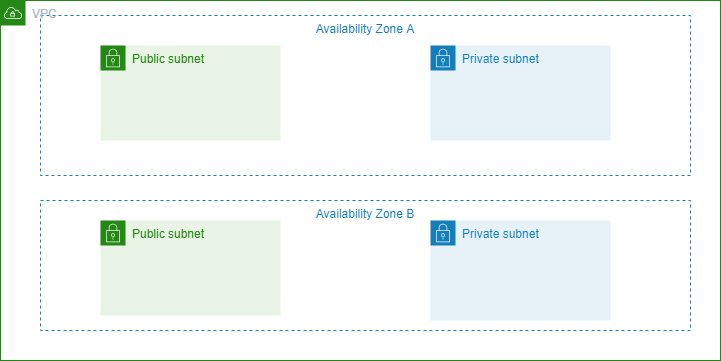
VPC-subnet
Requirements for CDK
In order to work with the cdk we will need 2 things, nodejs and the other is of course .NET 5 or 6. If you have nodejs and .net 5 or 6 ready then all you have to do is open your command line terminal and execute the following command to install cdk.
|
1 |
$npm install -g aws-cdk |
Now that the cdk is ready lets create a directory and intiliaze our application creation.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
$mkdir CdkVpcSample $cd CdkVpcSample $cdk init app --language csharp # Welcome to your CDK C# project! This is a blank project for C# development with CDK. The `cdk.json` file tells the CDK Toolkit how to execute your app. It uses the [.NET Core CLI](https://docs.microsoft.com/dotnet/articles/core/) to compile and execute your project. ## Useful commands * `dotnet build src` compile this app * `cdk deploy` deploy this stack to your default AWS account/region * `cdk diff` compare deployed stack with current state * `cdk synth` emits the synthesized CloudFormation template |
Lets take a look at what was created.
Below we have a list of generated application has created.
- A cdk.json file, with AWS CDK configuration
- A README.md file with some documentation that you may add for your project
- A src folder with the C# application
- A CdkVpcSample folder with the generated C# code
- Program.cs contains the main file., where we define how we will connect to our cloud env.
- CdkVpcSampleStack.cs contains the code for one CloudFormation stack (a stack is a collection of AWS resources that you can manage as a single unit), we use this to create the stack that we want.
- CdkVpcSample.csproj is the project file.
- GlobalSuppressions.cs deactivates one compiler warning.
- Last but not least the solution file, CdkVpcSample.sln
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
│ .gitignore │ cdk.json │ README.md │ └───src │ CdkVpcSample.sln │ └───CdkVpcSample CdkVpcSample.csproj CdkVpcSampleStack.cs GlobalSuppressions.cs Program.cs |
We can now open the sln file in our visual studio and lets modify the Program.cs file. We will modify the code to use the Account Id that you have for AWS and also the Region you plan to use. If you wish to use Env variables you can use the first block also. For simplicity sake I am using the second block to target only the region I plan to use.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
sealed class Program { public static void Main(string[] args) { var app = new App(); new CdkVpcSampleStack(app, "CdkVpcSampleStack", new StackProps { // If you don't specify 'env', this stack will be environment-agnostic. // Account/Region-dependent features and context lookups will not work, // but a single synthesized template can be deployed anywhere. // Uncomment the next block to specialize this stack for the AWS Account // and Region that are implied by the current CLI configuration. /* Env = new Amazon.CDK.Environment { Account = System.Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT"), Region = System.Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CDK_DEFAULT_REGION"), } */ // Uncomment the next block if you know exactly what Account and Region you // want to deploy the stack to. Env = new Amazon.CDK.Environment { Account = "123456789012", //fill in your account here Region = "us-east-1", //fill in the region you plan to use } // For more information, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/environments.html }); app.Synth(); } } |
Now we can jump into CdkVpcSampleStack.cs file and add the code we wish to create the vpc. We will also use nuget to install the Amazon.CDK.AWS.EC2 package.
You can also just use Visual Studio and add the package through the UI, just search Amazon.CDK.AWS.EC2 and click on install.
|
1 |
PM> Install-Package Amazon.CDK.AWS.EC2 |
Below is the vpc code that we will add to our CdkVpcSampleStack.cs file. Below we are creating a VPC with a CIDR 10.0.0.0/16 and 2 subnet one is public subnet with CIDR Mask of 24 and a private with a CIDR Mask of 24.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
using Amazon.CDK; using Amazon.CDK.AWS.EC2; namespace CdkVpcSample { public class CdkVpcSampleStack : Stack { internal CdkVpcSampleStack(Construct scope, string id, IStackProps props = null) : base(scope, id, props) { var vpc = new Vpc(this, "MyVpcSample", new VpcProps { Cidr = "10.0.0.0/16", MaxAzs = 2, SubnetConfiguration = new ISubnetConfiguration[] { new SubnetConfiguration { CidrMask = 24, SubnetType = SubnetType.PUBLIC, Name = "MyPublicSubnet" }, new SubnetConfiguration { CidrMask = 24, SubnetType = SubnetType.PRIVATE, Name = "MyPrivateSubnet" } } }); } } } |
Let’s now try to build the project going to the root directory where src directory is and type in command line
|
1 |
$ dotnet build src |
How do deploy
In order to deploy first you will need a user who has programmatic access to your aws account. Reach into the IAM service on AWS console and create a user. You can read my other IAM post on how to create a user.
Once created you can use aws cli to configure the user you will use like below I have used an access key id and secret access for it.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
PS C:> & 'C:\Program Files\Amazon\AWSCLIV2\aws.exe' configure AWS Access Key ID [None]: XYZS3CMdsgfdshdshdshggfdsdsgf AWS Secret Access Key [None]: z/DZTQpT6Zaasfdasfdasgasgdhfertdgf Default region name [None]: eu-central-1 Default output format [None]: json |
Now you can finally deploy with cdk using the cdk deploy command.
If you now login to the AWS console you will see in Cloudformation section that your Stack was created, and also in your VPC section the VPC was create with public and private subnet.
Challenges
- How to destroy the stack can you use cdk?
- What happens when you do cdk deploy again
- Change the Subnet CIDR to a different range
- Play around with the MaxAzs option
Summary
I hope this helps in teaching and learning how to deploy a VPC using AWS CDK to create a VPC in C#, we will continue on with explorer more on CDK with .NET in the following with AWS RDS Database.
Source code located at https://github.com/taswar/AWSCDKSamples/tree/main/CdkVpcSample



Leave A Comment